Web3
12 minutes
Advanced
The development of web technologies has brought numerous benefits to life and society, such as easier access to information, the emergence of new communication models, convenient access to services and entertainment, and the creation of new jobs through the reorientation of the economy.
According to the Pew Research Center, 42% of surveyed Americans believe that over the last 50 years, technology has brought more progress than other areas in improving quality of life.
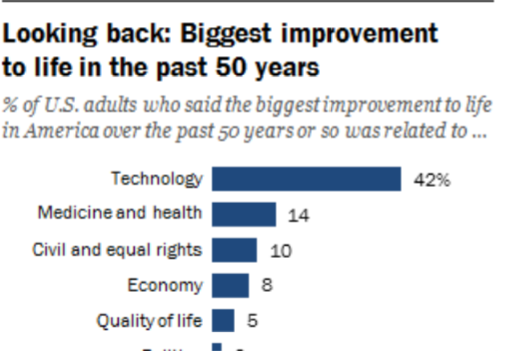
Despite the improvement in quality of life and numerous benefits of modern internet, we are faced with negative consequences of this situation. The companies, which have finally achieved the status of large enterprises, were responsible for building the existing online infrastructure. This centralized approach created a convenient and resilient infrastructure, but it has also introduced some problems and moved away from the original philosophy.
According to the "father" of the modern World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee, he envisioned the network as an open platform that allows anyone to exchange information and collaborate regardless of location, availability, or cultural background. However, the network has moved away from this perspective and faced three main problems:
- Loss of control over personal data;
- rapid spread of misinformation;
- The opacity of political advertising.
All of these problems are the result of the business models and centralized nature of the modern network. This has led to the search for a solution, which has resulted in the creation of the Web3 concept.
What sets Web3 apart from Web1 and Web2?
The evolution of the Internet has been marked by periods of dominance of particular technology stacks. For convenience, these phases of the Internet are divided into three stages: Web1, Web2, and Web3.
Web1, read-only web (1991-2004)
Other attempts to create networks for people to exchange information preceded the emergence of the first stage of the modern internet's development. These were mainly government projects such as ARPANET and NSFNET.
In fact, the history of the modern Internet begins in 1989 when Tim Berners-Lee created the World Wide Web. Tim Berners-Lee proposed a global hypertext project, now known as the World Wide Web. The project envisioned the publication of hypertext documents linked together by hyperlinks.
But why does the countdown to Web1 typically begin in 1991? It's because in that year, the world's first website was hosted on the world's first web server.
We can describe Web1 in one phrase - Read-only. Users could only view pages and interact with the content. The Internet had not yet provided users with the ability to participate in content creation. They consumed only what appeared on web resources. No authorizations, trackers, or registrations. At the end of the Web1 era, forums and chats began to appear. This allowed users to participate in content creation themselves.
Web2: Read-write (2004-present)
In 2005, American publisher and open-source software activist Tim O'Reilly published the book "What Is Web 2.0". In the book, O'Reilly noted that the Internet was starting to see more and more sites united by ideas and a common principle.
The era of Web2 began in 2004 and continues to this day. Now, large corporations and users alike are joining in. The former have taken control of the Internet and started building online empires, while the latter have been given the ability to participate in content creation. Web2 operates on the principle of read/write on the web.
The internet introduced authorization and the ability to create an account on almost every website. Users started voluntarily leaving their data and giving consent for data collection in exchange for convenience and access to resources. On the other hand, companies were able to profit from the data by selling it to advertising agencies. Some opened their own, which helped fully concentrate profits in their hands.
In Web2, social features emerged: more and more resources allowed users to communicate with each other, exchange messages, and make calls. Personalization can also be attributed to socialization: users can customize their own profiles, add photos and posts to their pages, publish videos and articles in a special way. Users publish content and receive reactions and evaluations from other users in the form of likes and comments.
Web 3.0: read-write-own
Originally, the term Web3 was considered in the context of the Semantic Web proposed by Tim Berners-Lee. The goal of the Semantic Web is to make internet data machine-readable. This vision describes a network of interconnected data processing technologies. They enable people to create online data stores, create vocabularies, and write rules for processing data.
In 2007, the CEO of Netscape, Jason Calacanis, expanded on the components of the Web3 concept. In addition to the semantic web, it included the following concepts: decentralization, AI and machine learning, open-source software, freedom (absence of censorship), and ubiquity (Internet presence almost everywhere).
But with the emergence of blockchain technology, the Web3 concept has largely focused on the idea of decentralization. For example, in 2014, Gavin Wood (co-founder of Ethereum and founder of Polkadot) referred to Web3 as a "decentralized online ecosystem based on blockchain."
In summary, Web3 can be defined as the ability for users to own their data and content. While Web2 allowed for creating content and digital profiles, it did not allow full ownership. The goal of Web3 is to give users complete control over their data. The fundamental difference between Web3 and Web2 lies in the increased decentralization at all levels, including data storage and application usage.
Main Ideas of Web3
It is difficult to give an exact definition of what Web3 is. However, several fundamental ideas serve as its guiding principles.
- Web3 is decentralized: ownership of the internet is shared between its creators and users. Centralized institutions do not control it or own it.
- Web3 is permissionless: no one is excluded from participating in Web3, and everyone has equal access to it.
- Web3 has native payments: it does not rely on outdated banking and payment system infrastructure. It uses cryptocurrencies for online spending and sending funds.
- Web3 is trustless: instead of relying on trusted third parties, it operates through incentives and economic systems. This is achieved through the use of Web3 technologies and concepts.
To bring the ideas of the new Internet to life, we need a set of Web3 technologies.
First and foremost, there's blockchain technology. Blockchain is a distributed database that can be accessed by anyone. This is called "distributed ledger technology." There is no centralized body or regulator that can control the blockchain at its own discretion.
Blockchain, in turn, powers the main technology used by users - decentralized applications (Dapps). They are similar to Web2 applications, but have the following unique features:
- Running on the blockchain
- Smart contracts
- They have open-source code
Above, we mentioned smart contracts, which are also one of the core technologies. A smart contract is a computer algorithm designed to create and maintain self-executing contracts, executed in a blockchain environment. Smart contracts eliminate intermediaries and implement the idea of a trustless environment. You can read more about smart contracts in our post.
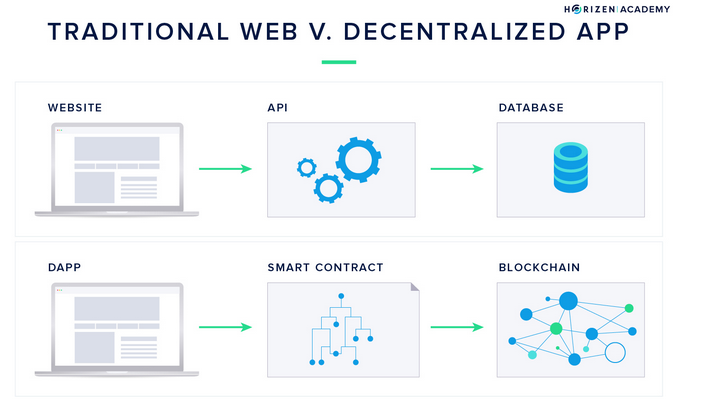
This is not a complete list of technologies, but rather the main components of the Web3 system. These technologies are changing three parts of the existing internet:
- Identity
- Economy
- Control
Right now, online identity is not universal and is not actually owned by the user. For example, if you want to post the same photo in all your social media profiles, you have to do it separately in each application. The concept of SSI (Self-Sovereign Identity) aims to solve this problem.
When successfully implemented, this concept will create a digital user profile with data that no one can read or modify without their permission. The user will be able to create their universal identity in a certain service. After that, when interacting with different dApps, they will "understand" that there is a real person behind the Identity and that it is your identity. In addition, your identity in the world of Web3 technologies will be cross-platform. You can use your identity everywhere, for this you just need to register once. Also, thanks to Identity and tokenization, any digital item can become cross-platform. For example, you can transfer a sword from one game to another. The Ethereum address and ENS profile already allow you to create a single account for the entire platform.
New technologies will also impact the economy. The Internet is already filled with a huge number of transactions used to pay for services and goods. However, the ability to make a transaction still depends on a centralized intermediary. A bank or government can block your card and assets. To solve this problem, cryptocurrencies are used. They speed up transactions, eliminate intermediaries, leave full control over funds to users, and also track transaction flows using special scans.
The next area to be impacted by changes is governance. Centralization in this area is a source of problems in the overall infrastructure. Web3 aims to solve this problem with decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). Web3 assumes that all organizations, companies, services, and applications will be DAOs. They do not have a CEO or board of directors. They have users, each of whom has the right to vote. Project development, content blocking, collaboration - all elements of the life of any organization will be decided through voting. There are different approaches to how many votes a user can have, but many of them focus on owning tokens in the project.
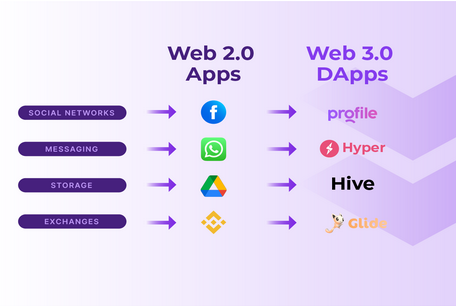
Examples of Web3 Usage
Web3 is already gradually penetrating into the areas of our lives and changing familiar spheres. Here are some examples of Web3 in real-life applications:
Wallets
This is a fundamental application in the world of Web3. With it, you store your assets, make transactions, and access applications.
Defi
Traditional banks and financial services are being replaced by decentralized applications that provide financial services such as lending, deposit-taking, and exchange services.
Examples: Maker, 1Inch, Uniswap, and others.
Gamefi
Games are also gaining traction in the world of Web3 technologies. There are two main advantages of Web3 games: game assets belong only to you, and you can earn money while playing.
Examples: Axie, AlienWorlds, Decentraland and others.
Social
This category includes web3 browsers, social networks, as well as sports, educational, and other applications. The main advantages are that your data is stored in a decentralized way, your search history is visible only to you, and some applications help you earn money. You can also include various NFT projects here.
Examples: Brave, Opera Reborn 3, DSCVR, and others.
Advantages and disadvantages of Web3
As a result of the above, the following advantages of Web3 can be highlighted:
- Control over your personal data and assets;
- Society's influence on decision-making
- Ease of use of universal identity
- Confidentiality of information
- Fast and convenient money transfers due to the absence of intermediaries
However, at the moment, the development of Web3 faces some challenges:
- Decentralization Absence
Moxie Marlinspike, a cryptographer and the founder of the Signal messenger, noted that applications claiming decentralization rely on centralized services, such as servers and APIs, to function. Also, Twitter founder Jack Dorsey criticized the concept of Web3 for the influence of venture capitalists in the field, stating that it would never be truly decentralized. - Difficult adaptation for new users
At the moment, the Web3 infrastructure is not very welcoming to new users. This is influenced by the complexity of the technology, the lack of educational and adaptation practices, and complex interfaces. - Fees
Transactions are more accessible, but some of the key services have fees that are too high for ordinary users. For example, this is one of the key problems with Ethereum. - Government Regulation
The state is the apex of centralization in modern society. That is why this institution periodically tries to slow down the spread of decentralization technologies through legislative means. The most striking example is the inclusion of Tornado Cash on the US sanctions list. - Insufficient development of some technologies and concepts
The Web3 sphere is at an early stage of development, so there are many questions when applying its concepts in practice. A prime example is DAO voting models. Many of the models repeat the mistakes of traditional institutions, for example, a model based on the number of tokens on a user's balance. Imagine that a user buys up all the tokens and casts only one vote, then there can be no talk of decentralization or fair voting. However, people see these problems and come up with mechanisms to mitigate them (for example, Quadratic Voting).



